GFCI Protection Requirements: Mobile & Manufactured Homes 2020 NEC – 550.13(B)

By: Jerry Durham | May 05, 2020
The 2020 NEC now recognizes that GFCI protection for mobile and manufactured homes must be equal to that of stick-built and modular type dwellings. Construction Codes, in general, have always been less restrictive for mobile-type dwellings. This may be because mobile homes are often titled with the Motor Vehicle Department, and this type of housing is built, inspected, tested, and listed off-site at a manufacturing plant.
2017 NEC Requirements for Mobile and Manufactured Homes
In the 2017 NEC, Section 550.13(B) provided electricians with a list of locations requiring GFCI protection in and around mobile and manufactured homes. That list included: 
- Outdoors, including compartments accessible from outside the unit
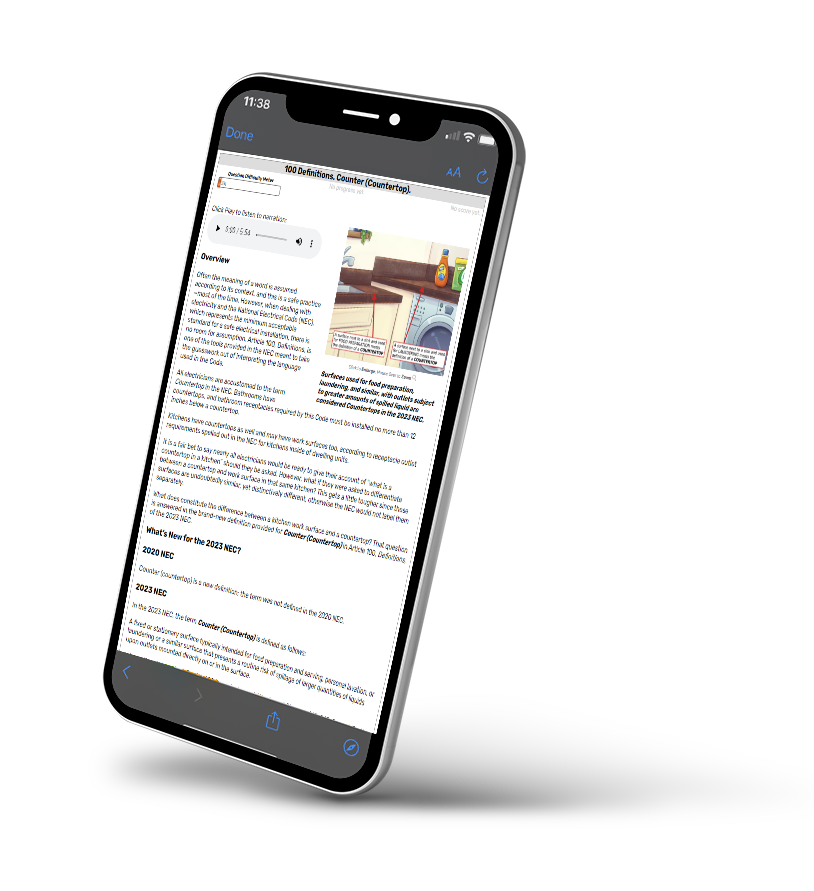
- Bathrooms, including receptacles in luminaires
- Kitchens, where receptacles are installed to serve countertop surfaces
- Sinks, where receptacles are installed within 1.8 m (6 ft) of the outer edge of the sink
- Dishwashers
At first glance, this list seems to cover all critical areas for the mobile or manufactured home. However, it leaves out important areas where GFCI protection is required in conventional, stick-built dwellings, like the underside of the home (crawl space) and receptacles in laundry areas.
2020 NEC Requirements for Mobile and Manufactured Homes
The 2020 NEC has closed that gap between mobile & manufactured homes and more conventional stick-built dwellings by requiring electricians servicing mobile-type dwellings to now follow the same GFCI protection requirements found in Section 210.8(A) that apply to the conventional stick-built dwelling.
Mobile and manufactured homes are no longer treated to a separate set of rules regarding GFCI protection.
What remains of Section 550.13(B) in the 2020 NEC?
Now that the list of locations requiring GFCI protection for mobile and manufactured homes has been removed from 550.13(B), two directives remain:
First: GFCI protection shall be as required in 210.8(A). Section 210.8(A) is of course the original list of 125- to 250-volt receptacles requiring GFCI protection in stick-built dwelling units.
Second: A short list of specific receptacles in mobile and manufactured homes that will NOT automatically defer to 210.8(A). Remember, 210.8(A) is a list of 125- to 250-volt receptacles that require GFCI protection, and it now applies to mobile and manufactured homes. The list of exceptions in 550.13(B) will ONLY apply to 125-volt receptacles within the mobile or manufactured home. It states: 550.13(B). GFCI protection shall not be required for other than 125-volt 15- and 20-amp receptacles installed within a mobile or manufactured home in the following areas:
- Compartments accessible from outside the unit
- Bathrooms, including receptacles in luminaires
- Kitchens, where receptacles are installed to serve countertop surfaces
- Sinks, where receptacles are installed within 1.8 m (6 ft) from the top inside edge of the sink
- Dishwashers
This means 250-volt receptacles in these locations within a mobile or manufactured home will NOT require GFCI protection. All other receptacles will need to defer to 210.8(A).
Comparing Mobile and Manufactured Home Requirements: 2017 NEC vs. 2020 NEC

Let’s now look at the six mobile & manufactured home locations that require GFCI protection in the 2020 Code cycle, that did NOT require GFCI protection in the 2017 Code cycle.
- Garages and accessory buildings with a floor at grade level
- Crawl spaces, at or below grade level
- Basements
- Boathouses
- Bathtubs and shower stalls where a receptacle is within 6 feet
- Laundry area(s)
The electrician can expect to provide GFCI protection for all of these 125- and 250-volt receptacles in mobile and manufactured homes when a permit is pulled under the 2020 Code cycle.
The 2020 NEC now recognizes that GFCI protection for mobile and manufactured homes must be equal to that of stick-built and modular type dwellings. Construction Codes, in general, have always been less restrictive for mobile-type dwellings. This may be because mobile homes are often titled with the Motor Vehicle Department, and this type of housing is built, inspected, tested, and listed off-site at a manufacturing plant.
2017 NEC Requirements for Mobile and Manufactured Homes
In the 2017 NEC, Section 550.13(B) provided electricians with a list of locations requiring GFCI protection in and around mobile and manufactured homes. That list included:
- Outdoors, including compartments accessible from outside the unit
- Bathrooms, including receptacles in luminaires
- Kitchens, where receptacles are installed to serve countertop surfaces
- Sinks, where receptacles are installed within 1.8 m (6 ft) of the outer edge of the sink
- Dishwashers
At first glance, this list seems to cover all critical areas for the mobile or manufactured home. However, it leaves out important areas where GFCI protection is required in conventional, stick-built dwellings, like the underside of the home (crawl space) and receptacles in laundry areas.
2020 NEC Requirements for Mobile and Manufactured Homes
The 2020 NEC has closed that gap between mobile & manufactured homes and more conventional stick-built dwellings by requiring electricians servicing mobile-type dwellings to now follow the same GFCI protection requirements found in Section 210.8(A) that apply to the conventional stick-built dwelling.
Mobile and manufactured homes are no longer treated to a separate set of rules regarding GFCI protection.
What remains of Section 550.13(B) in the 2020 NEC?
Now that the list of locations requiring GFCI protection for mobile and manufactured homes has been removed from 550.13(B), two directives remain:
First: GFCI protection shall be as required in 210.8(A). Section 210.8(A) is of course the original list of 125- to 250-volt receptacles requiring GFCI protection in stick-built dwelling units.
Second: A short list of specific receptacles in mobile and manufactured homes that will NOT automatically defer to 210.8(A). Remember, 210.8(A) is a list of 125- to 250-volt receptacles that require GFCI protection, and it now applies to mobile and manufactured homes. The list of exceptions in 550.13(B) will ONLY apply to 125-volt receptacles within the mobile or manufactured home. It states:
550.13(B). GFCI protection shall not be required for other than 125-volt 15- and 20-amp receptacles installed within a mobile or manufactured home in the following areas:
Compartments accessible from outside the unit
Bathrooms, including receptacles in luminaires
Kitchens, where receptacles are installed to serve countertop surfaces
Sinks, where receptacles are installed within 1.8 m (6 ft) from the top inside edge of the sink
Dishwashers
This means 250-volt receptacles in these locations within a mobile or manufactured home will NOT require GFCI protection. All other receptacles will need to defer to 210.8(A).
Comparing Mobile and Manufactured Home Requirements: 2017 NEC vs. 2020 NEC
Let’s now look at the six mobile & manufactured home locations that require GFCI protection in the 2020 Code cycle, that did NOT require GFCI protection in the 2017 Code cycle.
- Garages and accessory buildings with a floor at grade level
- Crawl spaces, at or below grade level
- Basements
- Boathouses
- Bathtubs and shower stalls where a receptacle is within 6 feet
- Laundry area(s)
The electrician can expect to provide GFCI protection for all of these 125- and 250-volt receptacles in mobile and manufactured homes when a permit is pulled under the 2020 Code cycle.


Are mobile and or manufactured homes built before the NEC’s 2020 code revision, say a 1992 manufactured home grandfathered until a GFCI needs replacement?